When we teach reading using what science (specifically the Science of Reading) tells us, we guide the brain to start recognizing and understanding those letters, syllables, and words. And the most effective reading comprehension strategies depend not only on explicit instruction, but on building background knowledge.
Comprehension instruction: Breaking it down
According to the Simple View of Reading, two cognitive capacities are required for proficient reading: (1) decoding, and (2) language comprehension.
“Reading comprehension is the product, not the sum, of those two components,” says Dr. Jane Oakhill, professor of experimental psychology at the University of Sussex. “If one of them is zero, then overall reading ability is going to be zero.”
As Oakhill explains further on Science of Reading: The Podcast, each component contains its own set of distinct skills and processes. It’s crucial to help students develop all of these capacities.
Building mental models for new information
Some readers are great at decoding but struggle with language comprehension. Why might that be—and how can you support them?
Here’s some context: After you read this paragraph, you aren’t likely to recall the precise wording—but you will probably remember the idea. Researchers use the term mental model to describe the cognitive strategies for the structure you create in your mind to perform this feat of comprehension.
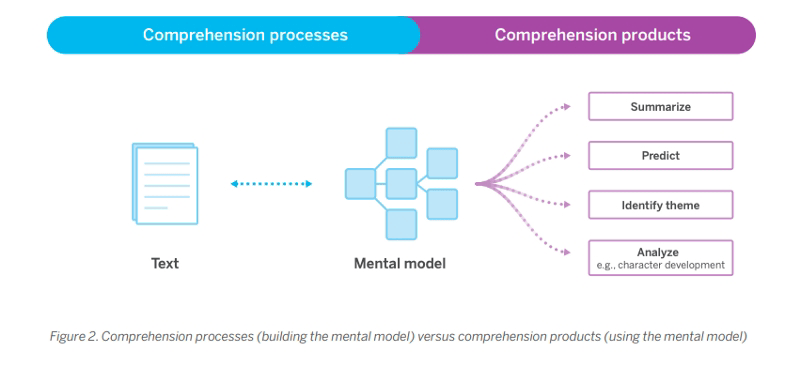
Historically, educators have thought about the process of comprehension — everything that happens after each word is recognized — as a black box. But now we know that there are two levels of comprehension at work: comprehension processes and comprehension products.
Comprehension processes are the steps you take to build a mental model of a text during reading. Comprehension products refer to the work you are able to do with that model after reading.
Think of the process of building a mental model as a sort of micro-comprehension. Weaker comprehenders build weaker models, so they may struggle when asked to create a narrative text summary, identify a theme, put together predictions, or describe key details of a character’s evolving beliefs.
By actively engaging with text, connecting prior knowledge, utilizing graphic organizers, receiving explicit instruction, and exploring new information, students can learn to build robust mental models that enhance their comprehension of the text. These mental models serve as frameworks for understanding, organizing, and synthesizing information, which then leads to improved comprehension, retention, and critical thinking.
Researchers have identified as many as 17 comprehension processes that affect students’ ability to build and use their mental models. The following are a few of the comprehension processes that weak comprehenders most commonly struggle with, and that with practice, can be targeted for skill development and improved overall comprehension.
- Anaphora (using pronouns to refer to an earlier word or phrase): Some readers struggle to process pronoun relationships (Megherbi & Ehrlich, 2005), identify antecedents, and answer questions that require resolution of anaphora (Yuill & Oakhill, 1988).
- Gap-filling inference: When reading the sentence “Carla forgot her umbrella and got soaking wet,” more skilled readers will conclude that it rained. A lack of awareness of when and how to activate background knowledge to fill in gaps may hinder a student’s ability to make inferences and comprehend the text as a whole (Cain & Oakhill, 1999).
- Marker words: Writers use connective words (e.g., so, though, and yet), structure cues (e.g., meanwhile), and predictive cues (e.g., “There are three reasons why…”) to signal ways that text fits together. Students with limited knowledge of the meaning and function of these words may struggle with the meaning of the text (Oakhill, et al., 2015).
- Comprehension monitoring: When proficient readers encounter difficulty, they tend to stop, reread, and try to figure it out. Less proficient readers may just keep going or fail to recognize that what they’re reading doesn’t fit their mental model.
Two strategies that you can employ in your classroom to guide students in comprehension strategy instruction:
- Graphic organizers: Use graphic organizers such as concept maps, story maps, or Venn diagrams to help students learn to visually organize information and relationships within the text. Visualization enhances comprehension (Graesser, et al., 1994). As the text progresses, students can refer to and update their models.
- Comprehension monitoring: Teach readers to monitor their comprehension while reading by pausing to reflect on their understanding, clarify confusing points, and adjust their reading strategies as needed. Monitoring comprehension helps good readers stay engaged and actively construct meaning from the text.
How background knowledge powers comprehension
The Science of Reading demonstrates the importance of systematic and explicit phonics instruction. But students don’t have to learn phonics or decoding before knowledge comes into the equation. In fact, the opposite might even be true.
Let’s say you’re handed a passage of text describing part of a baseball game. You read the text, and then you’re asked to reenact that part of the game. Which is most likely to help you do so?
- Your ability to read
- Your knowledge of baseball
- Neither
If you answered “2,” you’re batting 1,000. This example summarizes an influential 1988 study that concluded that the strongest predictor of comprehension was knowledge. In the study, which showed readers (with varying degrees of background knowledge about baseball) a passage describing a game, struggling readers comprehended as well as strong readers—as long as they had prior knowledge of baseball.
“The background knowledge that children bring to a text is also a contributor to language comprehension,” says Sonia Cabell, Ph.D., an associate professor at Florida State University’s School of Teacher Education, on Science of Reading: The Podcast.
In fact, background knowledge is the scaffolding upon which readers build connections between prior knowledge and new words. Students with average reading ability and some background knowledge of a topic will generally comprehend a text on that topic as well as stronger readers who lack that knowledge.
But until recently, literacy instruction has typically focused on decontextualized skills—finding the main idea, making inferences—rather than on the content of texts and resources that students engage with. According to Cabell, what we know about knowledge and comprehension should inform instruction for the whole class. “I think most, if not every, theory of reading comprehension implicates knowledge,” she says. “But that hasn’t necessarily been translated into all of our instructional approaches.”
How can we help build background knowledge while teaching reading? Here are some strategies backed by science.
- Systematically build the knowledge that will become background knowledge. Use a curriculum grounded in topics that build on one another. “When related concepts and vocabulary show up in texts, students are more likely to retain information and acquire new knowledge,” say education and literacy experts Barbara Davidson and David Liben. According to them, this retention even continues into subsequent grades. “Knowledge sticks best when it has associated knowledge to attach to.”
- Provide instruction that engages deeply with content. Research shows that students—and teachers, too—actually find this content-priority approach more rewarding than, in Davidson and Liben’s words, “jumping around from topic to topic in order to practice some comprehension strategy or skill.”
- Support students in acquiring vocabulary related to content. Presenting keywords and concepts prior to reading helps students comprehend text more deeply. Spending more time on each topic helps students learn more topic-related words and more general academic vocabulary they’ll encounter in other texts.
- Use comprehension strategies in service of the content. While building knowledge systematically, teachers can use proven strategies—such as chunking and creating graphic organizers—to help students develop skills they can use to support their for understanding of important information.
- Use discussions and writing to help students learn content. Invite students to share their interpretations, supporting their thought processes in their own words and connecting with peers’ perspectives.
- Help students forge connections in small groups. Help students draw connections between reading lessons and units—and their own experiences—as they grow their knowledge base together.
Every day, the Science of Reading has more to tell us about comprehension as a multifaceted skill that requires a combination of various strategies, tools, and techniques to unlock meaning from text. Because of this body of research, we know that when educators bring intentional and evidence-based practices into the classroom, students can enhance their ability to comprehend grade level text, analyze information critically, and engage with diverse subject areas. By nurturing students’ reading comprehension skills grounded in the Science of Reading, educators can empower students to become good readers who can navigate complex texts with confidence and understanding.
Explore more
The Amplify blog:
Science of Reading: The Podcast
- Background knowledge and education reform with Robert Pondiscio
- Deconstructing the Reading Rope: Background knowledge with Susan Neuman