RF.1.2.C.iii: Isolate and Pronounce Medial Sounds in CCVC, CVCC, CCVCC, CCCVC Words, etc.
Skill
RF.1.2.C.iii: Isolate and Pronounce Medial Sounds in CCVC, CVCC, CCVCC, CCCVC Words, etc.
Standard
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.2.C: Isolate and pronounce initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in spoken single-syllable words.
Description
- Mastery: Student can isolate and pronounce medial sound(s) of words with consonant blends.
- Acquiring: Student may not completely separate medial sound but may be able to state medial sounds of words with consonant blends with the help of the teacher.
Probes
T: What sound do you hear in the middle of ___? (clap: /ă/, print: /ĭ/, trunk: /ŭ/, switch: /ĭ/, plant: /ă/, scream: /ē/, sprung: /ŭ/, shrimp: /ĭ/, start: /ar/, splash: /ă/)
T: Which words have the same medial sound (vowel medial sound)? splash, scream, plant
S: splash and plant
T: Which words have the same medial sound (consonant medial sound)? lesson, kitten, missing
S: lesson and missing
T: Tell me a word that has the /ĕ/ sound in the middle.
S: (e.g. blend, let, went)
T: Which one of these three words has a different middle sound than the others? swim, flute, swoon
S: swim
Activities and Resources
Small Group Instruction – Direct Instruction
PA.038 Move and Tell
P.023 Medial Phoneme Spin (Do not use the spinner, only orally)
PA.039 Phoneme Isolating – Sound Quest
Introduce Middle Sound Segmenting (use pictures of words with four+ phonemes)
Middle Sound Segmenting Accuracy (use pictures of words with four+ phonemes)
Beginning, Middle, End (use pictures of words with four+ phonemes)
Elkonin Boxes with a Focus on Medial Sounds
Tap it, Map it, Hear it, Zap it!
Identifying Sounds in Words with Elkonin Boxes (with Pictures)
During Transition
Reinforce Skills/Independent Work Time – Independent/Small Group Center Activity
PA.011 Medial Phoneme Find
REVIEW: PA.039 Sound Quest (isolate initial, final, and medial phonemes in words)
REVIEW: PA.012 Phoneme Quest (isolate initial, final, and medial phonemes in words)
PA.034 Phoneme Matching Sound Bags
Display (e.g., Anchor Chart):
 |
 |
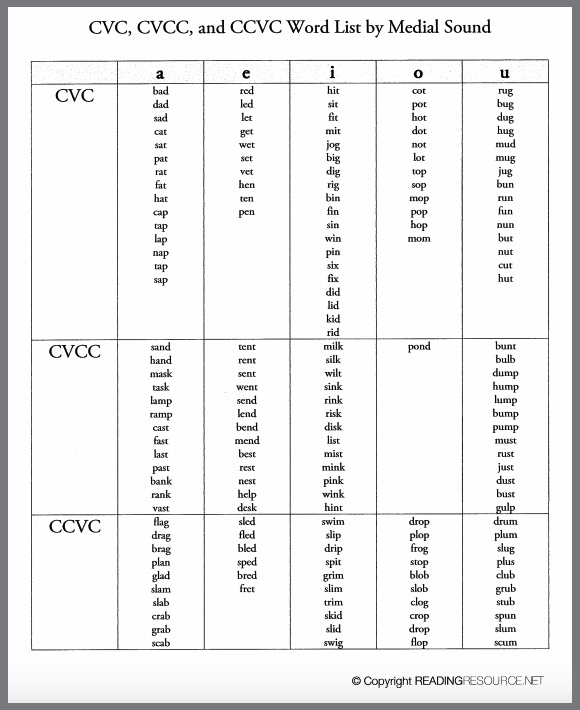
| Source: Reynoldburg City Schools (do not display – use as a resource for word bank) |
Source: Mrs. Gilchrist’s Class |
Considerations and Reminders
- Although there are many complex words to consider in this skill, remember that we are still practicing phonological awareness. Therefore, only the teacher should be looking at the word lists while students listen for the common medial sounds.
- Whenever students have to work with a stack of images make sure that students know the name of the images before using them in any activity. This is most important for English Language Learners (ELLs).
- ELLs might be discouraged when they encounter new (unfamiliar) words, however remind them that the focus in this skill is to listen to the sounds that they hear. If they can apply this skill to nonsense words and unfamiliar words, then they will have more success with subsequent skills.
- Depending on which language ELLs speak, some vowel sounds may be very difficult to produce (e.g., Spanish speakers may have difficulty producing the /ĭ/ as in pig). Use modeling and repetition to help students learn to pronounce new sounds.
- Teachers should be careful not add the schwa when pronouncing individual sounds for students.
- Elongating sounds in words can help students to segment words into individual phonemes.
- Use a variety of resources to demonstrate phoneme segmentation (e.g., a slinky, Elkonin boxes, and TPR).